Differential Diagnosis
In ECG interpretation, it is not uncommon to encounter situations where the available clinical information is insufficient to confirm a single diagnosis. In such cases, the typical approach is to list the possible diagnoses that the ECG tracing might suggest. This list of potential diagnoses is known as the differential diagnosis.
In the ECG Quiz, we handle differential diagnoses in a single interpretation in the following manner:
- At the Beginning Learning Level, diagnoses that make up the differential diagnosis are added as Should interpretations. Based on our scoring algorithm, the reader will receive credit for including these diagnoses in the interpretation but will not be penalized if not.
- At the Intermediate and Advanced Learning Levels, diagnoses that make up the differential diagnosis are added as Must interpretations. Based on our scoring algorithm, the reader will receive credit for including these diagnoses in their interpretation but will be penalized for omitting any diagnosis from the differential diagnosis in their interpretation.
Differential diagnoses differ from multiple interpretations. Multiple interpretations are used when ECG features may or may not be present, and these variations influence the interpretation.
An Illustrative Example
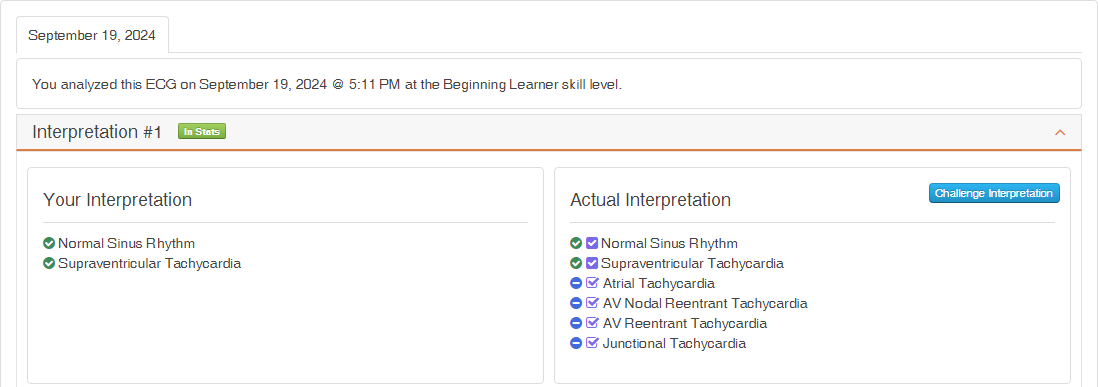
Consider the ECG in Figure 1, which contains a Normal Sinus Rhythm transitioning into Supraventricular Tachycardia. For this example, we assume the user submitted the following three diagnostic statements: Normal Sinus Rhythm, Atrial Tachycardia, and Junctional Tachycardia.

The results for the three diagnostic statements, when graded at the Beginner Level of Expertise, are shown in Figure 2. Notice that the user gets credit for all three diagnostic statements and is not penalized for omitting AV Nodal Tachycardia and AV Reentrant Tachycardia. Also, note that the user is not penalized for not submitting Supraventricular Tachycardia. For more details on how results are calculated and presented, refer to the Results Page.
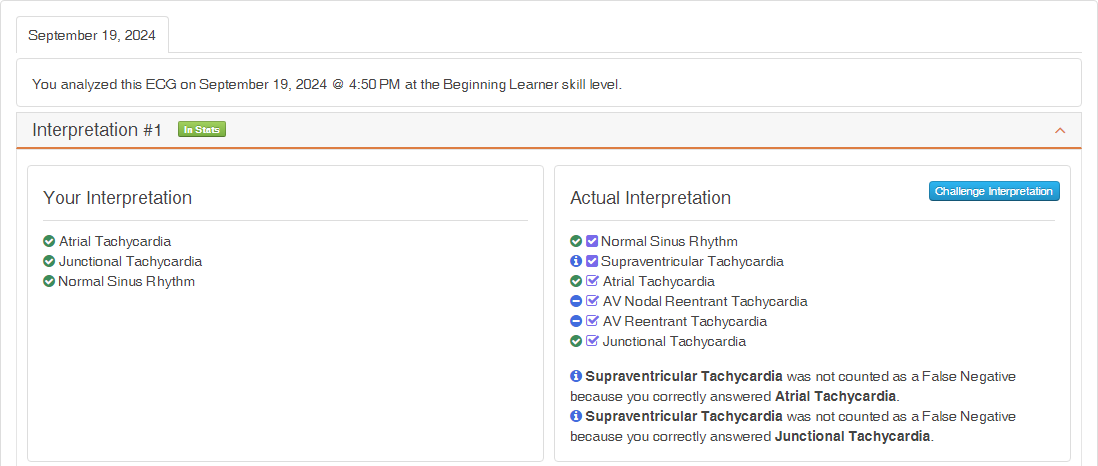
Figure 3 shows the results for the three diagnostic statements when graded at the Intermediate or Advanced Level of Expertise. While the user gets credit for the three diagnostic statements, they are penalized for not including AV Nodal Tachycardia and AV Reentrant Tachycardia.
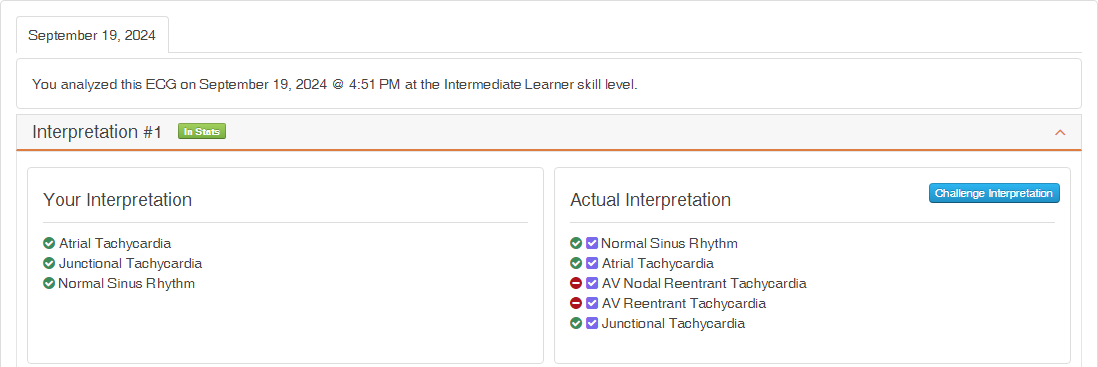
Now consider if a Beginner user only submitted Normal Sinus Rhythm and Supraventricular Tachycardia. Figure 4 shows the results for this scenario. The user gets credit for these two diagnostic statements and is not penalized for not entering any diagnostic statements that comprise the actual differential diagnosis.