Table of Contents
Differential Diagnosis
Interpreting ECGs often requires identifying more than one possible explanation for the observed features. When the available clinical or ECG information is insufficient to confirm a single definitive diagnosis, clinicians list all reasonable possibilities. This list is known as the differential diagnosis.
The ECG Quiz incorporates differential diagnoses directly into its scoring and feedback system. How differential diagnoses are treated depends on the selected Skill Level (see Skill Levels and Scoring Algorithm for details).
How Differential Diagnoses Are Handled
The ECG Quiz assigns items in the differential diagnosis as either Should or Must interpretations depending on the user’s skill level.
| Skill Level | How Differential Diagnoses Are Treated |
|---|---|
| Beginning Learner | Differential diagnoses are treated as Should interpretations. Users receive credit for including them but are not penalized if they do not. |
| Intermediate Learner | Differential diagnoses are treated as Must interpretations. Users receive credit for including them and are penalized for omissions. |
| Advanced Learner | Same as Intermediate. Differential diagnoses are treated as Must, and missing any required diagnosis results in a penalty. |
This structure ensures that beginners are not overwhelmed, while users at higher levels are held to the standards expected of experienced interpreters.
Differential Diagnoses vs. Multiple Interpretations
Differential diagnoses represent multiple possible explanations for a set of ECG findings.
Multiple interpretations, by contrast, represent variations in the ECG itself—for example, when a finding may or may not be present, and each possibility changes the interpretation.
See: Multiple Interpretations Explained
Illustrative Examples
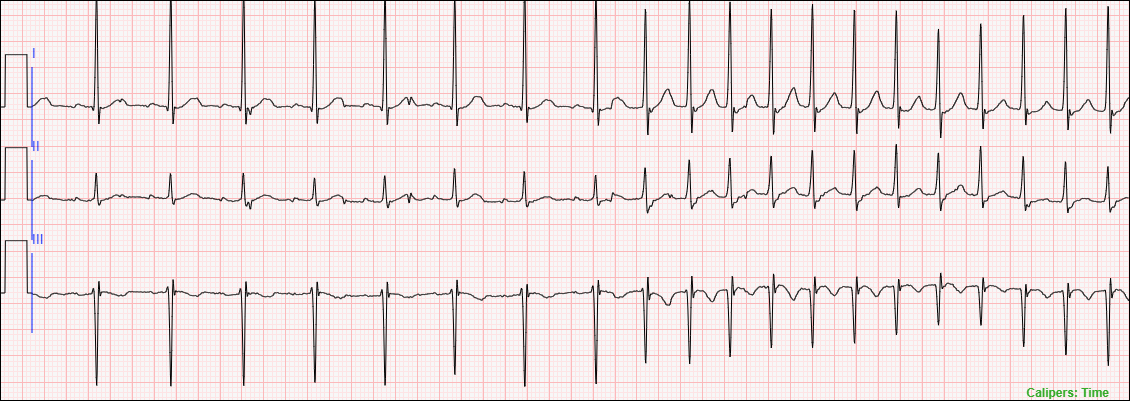
Consider the ECG in Figure 1, which shows a Normal Sinus Rhythm transitioning into a Supraventricular Tachycardia. Assume the user submitted the following three diagnostic statements:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Junctional Tachycardia
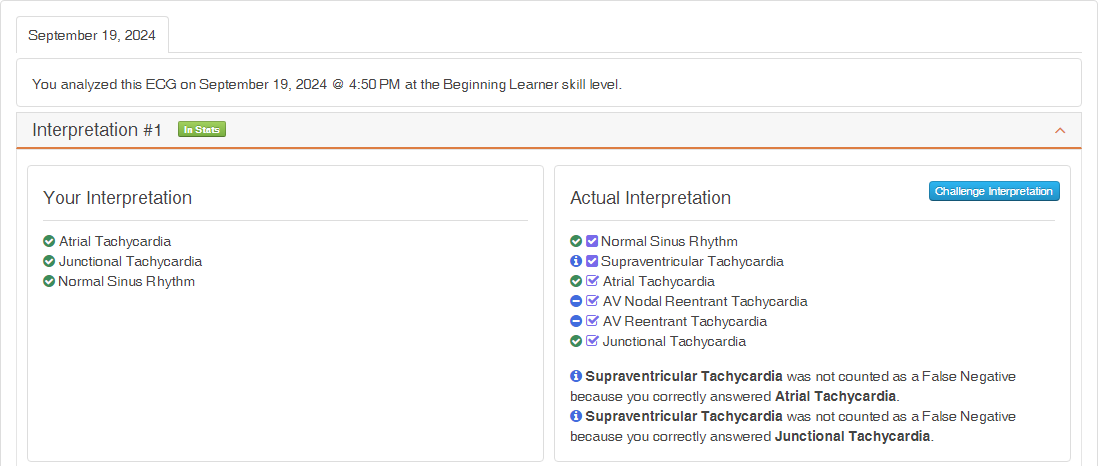
Beginner Skill Level
At the Beginner Level, differential diagnoses are treated as Should interpretations.
The user:
- Receives full credit for the three submitted diagnoses
- Is not penalized for omitting AV Nodal Tachycardia and AV Reentrant Tachycardia
- Is not penalized for not submitting Supraventricular Tachycardia
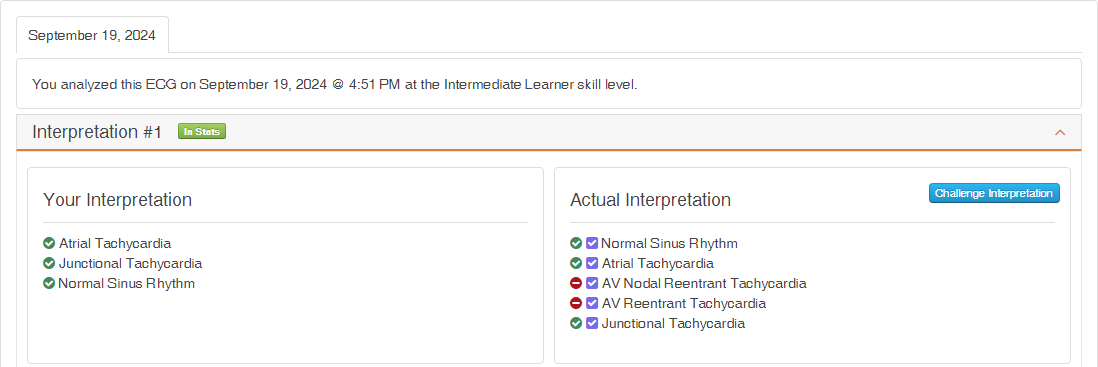
Intermediate and Advanced Skill Levels
At the Intermediate or Advanced levels, differential diagnoses are graded as Must interpretations.
Thus, although the user receives credit for their valid submissions, they are penalized for omitting:
- AV Nodal Tachycardia
- AV Reentrant Tachycardia
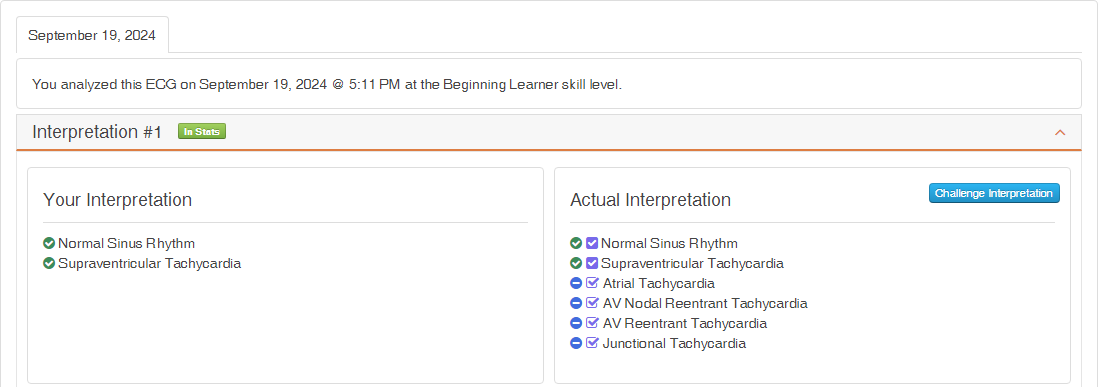
Additional Example: Beginner User, Simplified Entry
Now suppose a Beginner user submits only:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
Because the user is at the Beginner level:
- They receive full credit
- They are not penalized for omitting any other differential diagnoses
Key Takeaways
- Differential diagnoses allow multiple possible interpretations when certainty is limited.
- Differential diagnosis handling is directly linked to the user’s Skill Level.
- Beginners receive supportive, low-penalty scoring.
- Intermediate and Advanced users are expected to include all required components of the differential.
- Differential diagnoses differ from multiple interpretations, which address uncertainty about ECG features themselves.
Differential Diagnosis Rules and Scoring Outcomes Summary
The table below summarizes how Differential Diagnosis entries are handled across the three ECG Quiz Skill Levels and how each rule affects scoring, penalties, and interpretation outcomes.
| Skill Level | How Differential Diagnoses Are Treated | Credit Given for Including Dx? | Penalty for Omitting Required Dx? | Scoring Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginning Learner | Differential diagnoses are treated as Should interpretations | Yes — user receives credit for including any item in the differential | No — omissions are *not penalized* | Encourages exploration; protects beginners from penalties; supports early learning |
| Intermediate Learner | Differential diagnoses are treated as Must interpretations | Yes — user receives credit for each correct diagnosis | Yes — omissions produce False Negatives | Requires complete differential; missing diagnoses lowers accuracy score |
| Advanced Learner | Differential diagnoses are treated as Must interpretations | Yes — same as Intermediate | Yes — omissions produce False Negatives, sometimes multiple | Holds user to expert-level completeness and precision; strict scoring standard |
Interpretation Impact Summary
| Interpretation Behavior | Beginning Level | Intermediate Level | Advanced Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Differential items included | Credited as correct | Credited as correct | Credited as correct |
| Differential items missing | No penalty | Penalized | Penalized |
| Requirements for completeness | Partial differential acceptable | Must include all items | Must include all items |
| Scoring strictness | Low | Moderate | Highest |
| Primary educational goal | Build confidence, encourage recognition | Strengthen completeness and accuracy | Achieve expert-level precision |